Influence of the lamination process on the mechanical properties of a PA6 electronspun membrane filter and its filtration capability
Polyamide 6 (PA6) nanofiber hybrid membranes have demonstrated excellent filtering capability. Recently, increasing attention has been given to hydrophilic membranes such as PA6 in applications. Unfortunately, PA6 has not found any real application due to its poor mechanical strength under high pressure. In this study, PA6 nanofiber layer has been prepared using wire electrospinning method. Three supporting materials with different adhesion methods have been used to improve the mechanical properties of the membranes.
The fibers were electrospun by using a continuous rotary wire extrusion (CRE) method. Three supporting materials with different adhesion method has been used to improve the mechanical properties of the membranes. Mechanical properties of PA6 nanofiber membrane was tested by tensile test and broken film method on glass slide under uniaxial compression, transverse expansion and extension at various angle. The filtration capability of PA6 nanofiber hybrids in various applications such as microfiltration, reverse osmosis was also investigated. The results showed that PA6 nanofiber hybrid membranes had better mechanical strength compared with its parent material
The development of electrospun nanofiber synthetic membrane allows synthesis of high surface area and high pore density. It also has a strong character. Therefore, it is an attractive alternative to other synthetic membranes suitable for applications such as reverse osmosis and ultrafiltration.
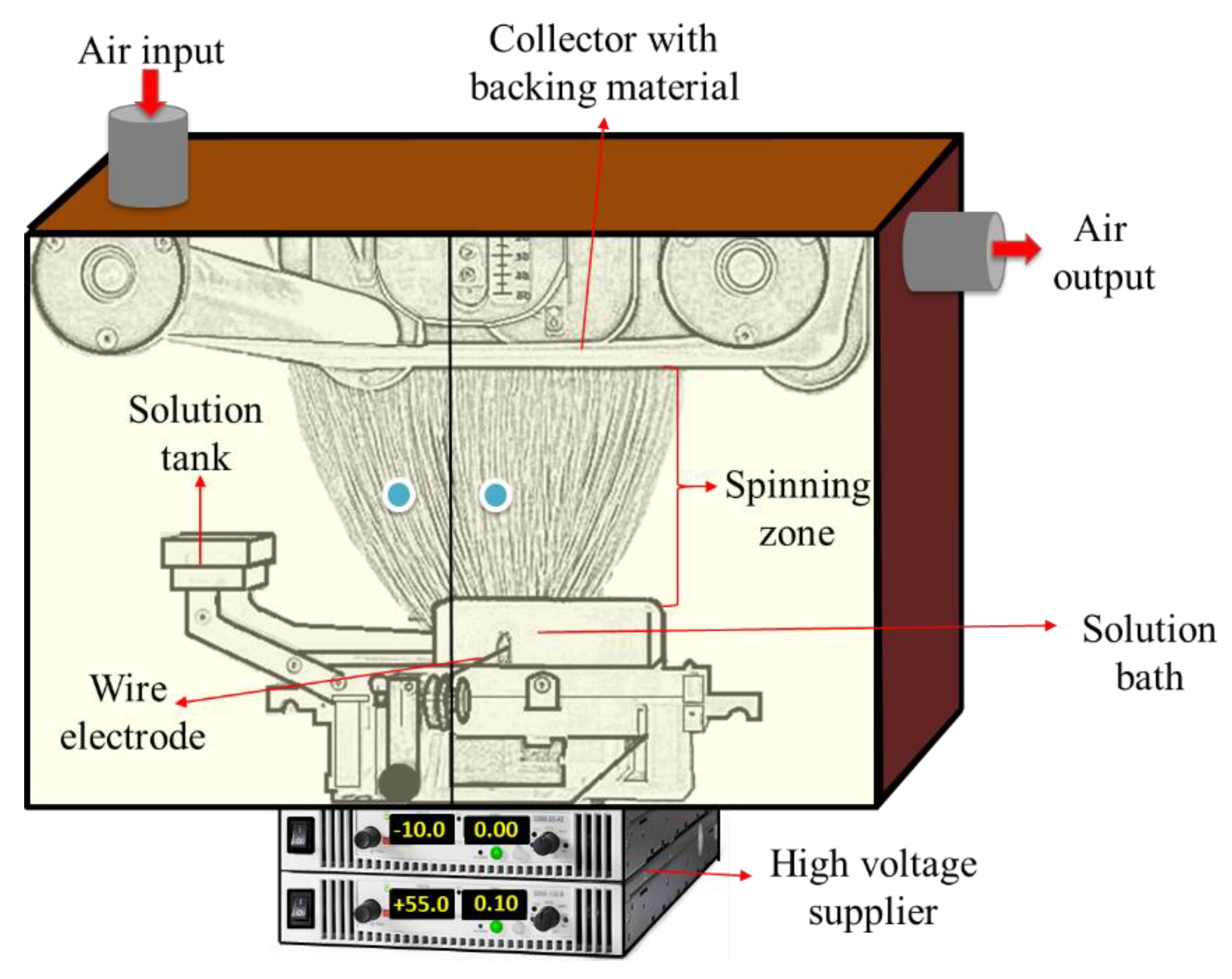
We have studied the impact of lamination process on the properties of a PA6 nanofiber membrane and its filtration capability. According to literature, the electrospinning principle is used in this study. We prepared 12 % wt. of PA6 (BASF-Ultramid B24, Germany) solution by dissolving polymer pellets in acetic acid/formic acid (2/1 % wt.) solvent mixture over night. All the solvents were purchased from Penta s.r.o (Prague, Czech Republic). The PA6 nanofiber layers were prepared using lab-scale wire electrospinning system. The principle of wire electrospinning system has been introduced to literature several times. In brief, the solution is placed in a solution tank which is closed system connected to solution bath with positive charge electrode 60 kV passing along metal orifice in middle of bath (Figure 1). There is adjacent solution bath with speed 240 mm/s which moved back and forward and fed surface of wire electrode with polymer solution
The use of PA6 nanofiber as membrane filter (MEF) has been widely studied in recent years. The design of membrane is the most important step for developing the MEFs with high content of functional groups and strong electrolytes, suitable for accurate water quality control. The current work focuses on investigating the influence of the lamination process on the mechanical properties of a PA6 electronspun membrane filter and its filtration capability.
The effects of the lamination process on the mechanical properties and filtration capability of PA6 nanofiber membranes were investigated by means of hardness, tensile strength and elongation at break tests. The samples prepared by using the non-lamination method exhibited slightly higher values for the Young’s moduli than those prepared using the lamination process. A combined effect of water content, extra surface hydrophilicity and lamination processes can be observed: The average values (in Water) of elastic modulus and loss tangent are significantly lower in PA6 nanofiber membrane prepared by solvent evaporation method compared to those prepared by electrospinning
The influence of the processing conditions on the electrospun polyamide nanofiber membrane's mechanical properties has been investigated. The polydispersed membranes were prepared at different weight percentages and a number of mechanical parameters as well as electrical conductance and filtration capability were recorded. The established process can be used to produce high quality nanofibrous membranes with a high percent of different functional groups and applications in various fields including material characterization, energy harvesting and filtration applications.
The influence of the lamination process on the mechanical properties of a PA6 electronspun membrane filter was studied. For this purpose, 12 % wt. of the polymer pellets in acetic acid/formic acid (2/1 % wt.) solvent mixture was prepared over the night by dissolving the polymer pellets in acetic acid/formic acid (2/1 % wt.) solvent mixture over the night. The resulting solution was filtered using microporous electrodes, which were prepared using a lab-scale wire electrospinning system. The principle of wire electrospinning system has been introduced to literature several times In brief, the solution is placed in a solution tank which is a closed system and connected to a solution bath. The positively charged wire electrode passes along a metal orifice that feeds back and forth across the solution bath. There is also a solution bath with a speed of 240 mm/s which is moved back and forth so as to feed back across off an area weight of 2 g/m2 plasticizer solution
The influence of the lamination process on the mechanical property and filtration quality of a PA6 nanofiber was investigated. The bromination process in polymer production led to the appearance of (3-bromo) propionic acid and its derivatives. Based on these results, it was suggested that bromide ions could be associated with PA6 fibers due to electrostatic forces between cations and electrons on the surface. The goal of this paper is to study the influence of a number of parameters on both mechanical properties and filtration quality
The influence of the lamination process on the mechanical properties of a PA6 electronspun membrane filter and its filtration capability. Nomenclature ALP-nameplate derivation: Alumina phase (1), Aluminum oxide phase (2), Carbon black polymer rich phase (3), Chromium oxide phase (4) Clay phase (5) Ferrite phase (6), Graphite oxide phase(7), Hydroxyl ionomer material (8), Magnetite phase(9) Mica phase (10), Magnesium oxidephase (11), Silicon carbide phase(12) Titanium diboride ceramic model material(13).
Here, we demonstrate the influence of the lamination process on the mechanical properties of a PA6 electronspun membrane filter and its filtration capability by comparing it with control samples prepared by only a single treatment. We also introduce two new methods to increase the mechanical strength of electron-sputtered nanofibers through their different approaches.
Story Source:
Materials provided by Case Studies in Chemical and Environmental Engineering. The original text of this story is licensed under a Creative Commons License. Note: Content may be edited for style and length.
Journal Reference:
- Yalcinkaya, F., Yalcinkaya, B., & Hruza, J. (2019). Electrospun Polyamide-6 Nanofiber Hybrid Membranes for Wastewater Treatment. Fibers and Polymers, 20(1), 93–99. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12221-019-8820-4
0 Comments